Assuming that "genetically“ is needed, became 8 results found.
Newsletter XLV 2023 - November 5th to 11th - News+ Are Habeck, Pistorius, Baerbock an infernal trio?
were repealed. It has never been clarified who the agitators were who incited the unemployed to pogrom. Doubts were even raised as to whether this even existed. * Pesticide | genetic | Plant protection New pesticide: This poison knocks out genes. Active ingredient kills Colorado beetles by interfering with the genome. US authorities shorten test phase. How the drug works and what dangers it poses...
If the species continues to exist in other places, it is a local extinction. A biological species becomes extinct when the last individual of the species dies. As a result, their genetic information is lost and biodiversity is reduced. The distinction between species extinction and mass extinction is unclear. Species extinction primarily refers to...
However, it is still being tested in pilot projects... * Evolution | Innovation Engine of evolution How our genome made us human It is a mystery of evolution: We hardly differ genetically from our closest relative, the chimpanzee - our genes are 98,7 percent similar. Nevertheless, our ancestors developed numerous skills and anatomical differences that...
did not want it. Not just because he was Jewish and Sigmund Freud's nephew. The Nazis, on the other hand, didn't mind something like that if necessary. To paraphrase Hermann Göring: “I decide who is a Jew.” Both genetic and intellectual reasons kept Edward Bernays away from the Nazis and drew him to psychoanalysis. In the USA, where his family immigrated from Vienna in 1892 when he was not yet one...
Newsletter XXXVII 2022 - September 17 to 23 - News+ Low-level ionizing radiation also poses a risk
Dose affects us, but continues to accumulate over time! * Dangers of ionizing radiation - Scientists refer to new data * Radiation effects on people * Genetic damage ** YouTube Keyword search: Low radiation genetic damage https://www.youtube.com/results?search_query=Low radiation+genetic+damage - - Videos: Federal Office for Radiation protection -...
17.03.2019/XNUMX/XNUMX - Deadly dust - use of uranium ammunition and the consequences
AIDS with increasing infectious diseases, - severe dysfunction of the kidneys and liver, - highly aggressive leukemias and other cancers, - disorders in the bone marrow, - as well as genetic defects and malformations with abortions and premature births in pregnant women, as we already saw after the Chernobyl disaster have. That is, a particularly terrible consequence of...
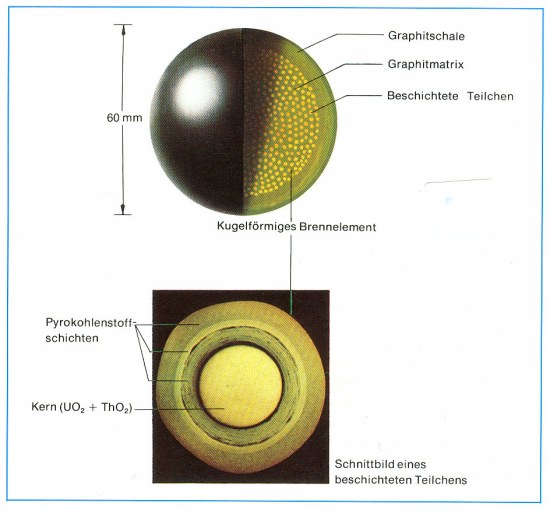
Studies on the THTR from 1986 to 2015
A sustained low dose is just as carcinogenic as a single higher acute exposure, as the researchers report in the specialist journal “Lancet Hematology”. more... 2013 - Radiation-induced genetic effects after Chernobyl and in the vicinity of nuclear facilities Study on "low-dose radiation" by the Munich Helmholtz Center from 2013 Conclusion: "Low-dose radiation" increases the...
What is low level radioactive radiation? INWORKS study
Radiation damage If ionizing radiation affects gonads (testicles or ovaries) or germ cells (sperm or egg cells), it can cause damage to their genetic material (mutations), which can lead to genetic diseases (hereditary damage). These can occur in the children and children's children of the irradiated people in the form of malformations, metabolic disorders, immune damage, etc.